Hypervisors
VMWare
The FortiPoC archive contains vmx and vmdk files for VMWare hosted products.
ESXi6.x
ESXi6.x doesn’t support the sparse file for VMWare hosted products. You must convert it to zeroedthick with vmkfstool.
VCenter
1GB Hugepages
If you need 1GB hugepages but instruction set is not exposed to FortiPoC you should try to edit the VM in VCenter, in “Edit settings/VM Options/Advanced/Configuration Parameters”:
featMask.vm.cpuid.pdpe1gb = Min:1
Note
this option exposes the instruction set but don’t enforce that VCenter is actually allocating hugepages to the FortiPoC.
Bridging with an external network with ESXi
Use case
See the network topology below:
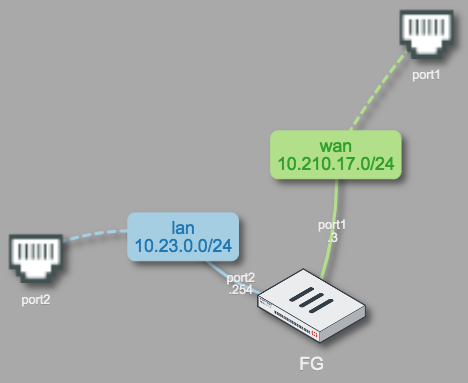
wan network is bridged with FortiPoC port1
lan network is bridged with FortiPoC port2
So, FG is connected with two external networks through its own port1 and port2. The fact that FG port1 is connected to FortiPoC port1 and the FG port2 to FortiPoC port2 is pure fortuity.
FortiPoC’s port1 and port2 are respectively tied to FortiPoC system interfaces eth1 and eth2.
These interfaces are connected to ESXi port groups which have all their default security parameters disabled.
Because the FortiPoC interfaces eth1 and eth2 have different MAC addresses than FG port1 and port2, you have to change the security parameters as specified below:
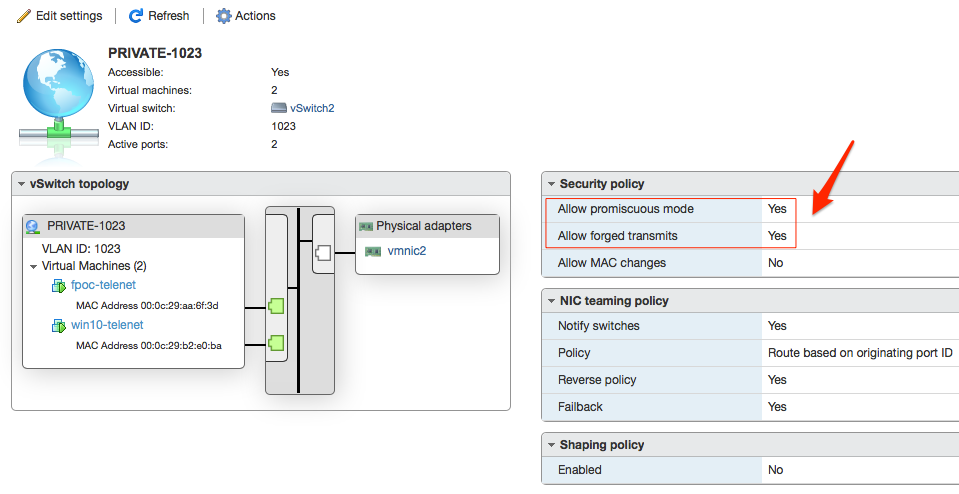
Allow forged transmits instructs ESXi to allow packet with FG Mac address to access the port group. This allow traffic from FG to external devices through this port group.
Allow promiscuous mode allows ESXI to accept ARP broadcast be flooded into the port group. This allow traffic from external devices to FG.
Qemu/KVM
Image conversion
You can use the vmdk to run under Qemu/KVM:
qemu-img convert -O qcow2 fortipoc.vmdk fortipoc.qcow2
You should at least define 4 virtio network interfaces (one management interface and 3 PoC external interfaces).
FortiPoC
CPU allocation
You can now easily assign set of cores to different group of processes:
system: the system group is where all the FortiPoC core processes (like Web GUI, monitoring tools, CLI, …) are running. The core 0 is always part of it and is automatically added
vm: for VMs only
lxc: for LXCs only
isolate: to isolate cores, VM must be explicitly pinned to CPUs in these cores to be able to use them
Once you have assigned a set of cores to a group with set cores
GROUP CORE[,CORE]* (accept COREn-COREm notation, example
3-5), FortiPoC will automatically try to use unassigned cores for
other groups.
Warning
as system cores are assigned at boot, system is always using all cores except if some are assigned to the system group and the FortiPoC instance is rebooted.
Cores list can overlap between the group, but it’s not recommended.
Here is an overview matrix:
Definition |
Assignment |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
system |
vm |
lxc |
isolate |
system |
vm |
lxc |
isolated |
|
none |
none |
none |
none |
all |
all |
all |
none |
|
SET1 |
none |
none |
none |
SET1 |
all - SET1 |
all - SET1 |
none |
|
SET1 |
SET2 |
none |
none |
SET1 |
SET2 |
all - SET1 - SET2 |
none |
|
SET1 |
none |
SET2 |
none |
SET1 |
all - SET1 - SET2 |
SET2 |
none |
|
SET1 |
none |
none |
SET2 |
SET1 |
all - SET1 - SET2 |
all - SET1 - SET2 |
SET2 |
|
none |
SET1 |
none |
none |
all |
SET1 |
all - SET1 |
none |
|
none |
none |
SET1 |
none |
all |
all - SET1 |
SET1 |
none |
|
none |
none |
none |
SET1 |
all - SET1 |
all - SET1 |
all - SET1 |
SET1 |
|
You can force CPUs set by device in the expert settings.
Hugepages Memory
To reserve some memory for hugepages usage, you must use set memory hugepages CLI command.
You can enable hugepages by device in the expert settings.